Understanding the influence of nutrition on health is a cornerstone in the fight against chronic diseases. As modern medicine continues to evolve, the role of personalized nutrition in managing conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity has become increasingly significant. This approach not only enhances individual health outcomes but also offers a promising pathway for …
Understanding the influence of nutrition on health is a cornerstone in the fight against chronic diseases. As modern medicine continues to evolve, the role of personalized nutrition in managing conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity has become increasingly significant. This approach not only enhances individual health outcomes but also offers a promising pathway for preventive care.
Understanding Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension affect millions globally and are influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. The interplay between these elements can accelerate or mitigate the progression of these diseases, underscoring the importance of lifestyle choices, particularly dietary habits, in managing chronic illness.
The Link Between Nutrition and Chronic Diseases
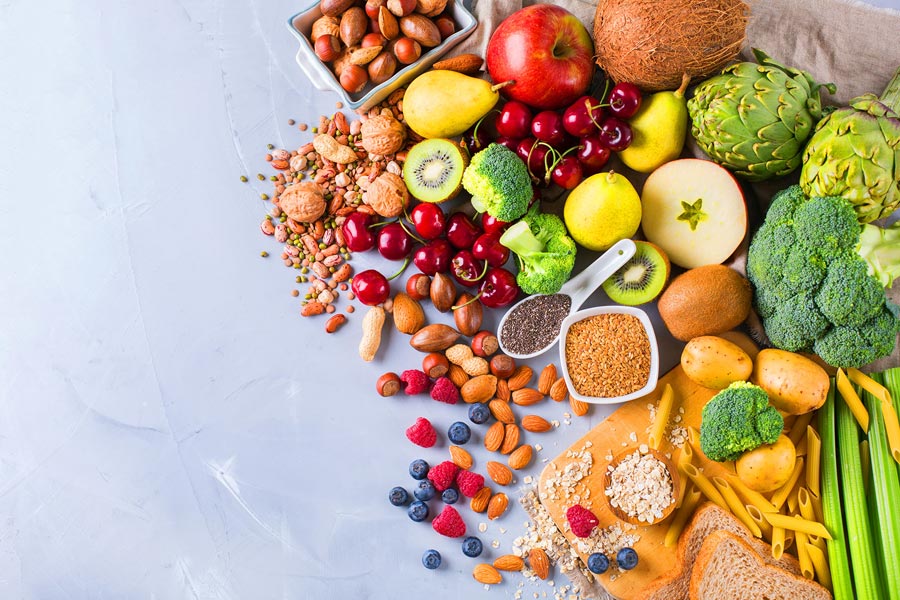
Dietary patterns and nutrient intake play crucial roles in the development and management of chronic diseases. Ample research, including epidemiological studies and clinical trials, supports nutrition’s effectiveness in preventing and managing these conditions. For instance, diets rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and diabetes, and in some cases, even reverse the effects of these conditions.
Key Nutrients for Disease Management
Certain nutrients and dietary components are particularly influential in managing chronic diseases:
- Fiber: Essential for digestive health and shown to help manage blood sugar levels, thus aiding in diabetes control.
- Antioxidants: Help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, underlying factors in many chronic diseases.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, beneficial for heart health and joint pain relief.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Specific vitamins and minerals, such as potassium and magnesium, can help manage blood pressure and support overall cellular function.
A balanced diet incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is foundational for managing and potentially reversing chronic conditions.
Nutritional Strategies for Disease Management
Tailoring diet plans to specific chronic conditions can significantly enhance management efficacy. For instance:
- Heart-Healthy Diets: Emphasize low sodium intake, abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Diabetes Management Plans: Focus on balancing carbohydrate intake with whole foods to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Weight Management Strategies: Prioritize portion control, regular meal timings, and balanced macronutrient distribution.
- Hypertension-Lowering Diets: Reduce salt intake and increase consumption of potassium-rich foods.
Incorporating mindful eating and consistent meal planning plays a crucial role in adhering to these dietary strategies effectively.
The Role of Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations to individual characteristics like genetics, metabolic profile, and lifestyle, enhancing the efficacy of dietary interventions. Innovations in nutrigenomics and wearable technology are paving the way for more customized nutrition advice that aligns closely with individual health needs and goals.
Integrating Nutrition into Healthcare Practice
Integrating comprehensive nutrition counseling and support in healthcare settings is essential for effective chronic disease management. Collaboration among doctors, dietitians, nutritionists, and behavioral specialists is crucial to provide patients with holistic care that extends beyond traditional medication.
Community Engagement and Public Health Initiatives
Community programs and public health initiatives play pivotal roles in promoting healthy dietary habits. Educating communities about nutrition, providing access to healthy foods, and implementing policies that encourage healthy lifestyle choices are fundamental in mitigating the prevalence of chronic diseases.
Conclusion
Nutrition is not just a pillar of health; it’s a powerful tool in managing and preventing chronic diseases. Emphasizing nutrition education and integrating dietary counseling into healthcare can profoundly impact public health. As we continue to understand more about the intricate connections between diet and chronic disease, it becomes clear that empowering healthcare providers and individuals with nutritional knowledge is essential for fostering longer, healthier lives.